Diamonds
The Four C’s
Cut
Cut refers to the shape that the diamond is cut into and the quality of the cutting. When a diamond is poorly cut, instead of the light reflecting and refracting off the facets back up through the table, the light is lost out the back or the sides of the diamond making the stone look dull and lifeless.
The diamond cut is often required as the most important of the four C’s as even the cleanest, whitest diamonds can look low graded when poorly cut. To avoid this we only select diamonds with an excellent cutting grade

Colour
Diamonds are colour graded from D-Z. The highest diamond grade is D which is classed as colourless whist M and below is classed as light yellow or light brown. Whilst there is a slight colour difference from D-H, this range of colour is generally seen as rare white, with colour becoming apparent in grades I and below
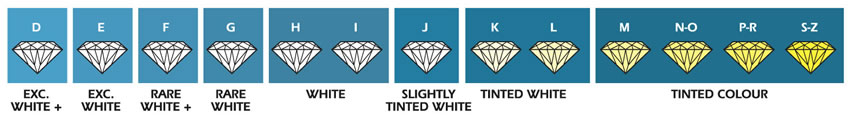
Fancy coloured diamonds also occur naturally most commonly champagne, chocolate and yellow diamonds. Less common are the pink, green and blue natural colours. Diamonds can also be treated to induce these rearer colours in laboratories.
Clarity
All diamonds contain imperfections. The very best, and rarest, clarity is Flawless (FL). Because many inclusions are not visible to the naked eye, diamonds are graded under 10 x magnifications.
For grade SI and above inclusions are only visible under a 10X magnification. When the clarity grade drops to I1 and under, inclusions becomes visible to the naked eye.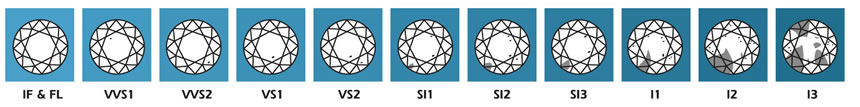
Carat
Diamond weight is measured in carats and 100pts = 1 ct.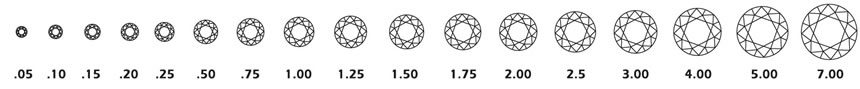
Learning Centres
Both the Gemmological Association of America - www.gia.edu/
and the British Gemmological Association - www.gem-a.com/education.aspx
are highly regarded institutions in the world of gemstone education .
Conflict-free
At Berry’s all our diamonds are 100% conflict-free and have been imported in accordance to the Kimberley process. Our diamonds are sourced from well-known legitimate suppliers against the funding of conflict through the sale of diamonds. All diamonds weighing over 0.30ct come with a full diamond report and certificate from one of the following institutes and can be traced back to its origins.
Gemological Institute of America (GIA)
Diamond High Council of Belgium (HRD)
Quasar Diamonds (NZ)
Premier Certificates (NZ)
It is now accepted internationally that along with the Kimberley Process there should be a chain of warranties from mine to wholesaler to retailer that gives the consumer the assurance that the diamonds they are purchasing are “conflict free”.
It should be noted however that there are many commercial benefits associated with the diamond industry in many developing countries. This industry has provided employment, infrastructure such as roads, as well as funding for hospitals and educational facilities.
The following is an outline of: Ensuring a Conflict-Free Diamond Industry.
Mining / Export – Kimberley Process Certification (KP) Rough diamonds traded between KP countries are transported in a tamper-resistant container and accompanied by a government validated KP Certificate.
Import / Manufacturing / Retail – System of Warranties Assurance (SoW) Once imported and ready to be traded, a written statement must accompany all invoices guaranteeing that the diamonds or diamond jewellery being sold are from legitimate sources.
What are conflict diamonds? Diamonds that are illegally traded to fund conflict, such as civil war. The term originated in the 1990s when rebels in some African countries used diamonds to fund movements against legitimate governments. At the height of the problem conflict diamonds accounted for only 4% of the world diamond supply. Today they account for considerably less than 1%.
What has been done about conflict diamonds? The diamond industry, governments, the United Nations and non-governmental organisations adopted the Kimberley Process Certification System to stem the trade in conflict diamonds. The System of Warranties was put in place to assure only legitimately sourced diamonds are traded. Today over 99% of the worlds diamond supply is certified to be from sources that are free from conflict.
New Zealand & the Kimberley Process It is important to note that New Zealand is a signatory to the Kimberley Process United Nations Sanctions Regulations 2004. These regulations came into effect in New Zealand on 14 January 2005. This regulation ensures that rough diamonds may be imported into, or exported from, New Zealand, only in accordance with the Kimberley Process Certification System adopted under the Interlaken Declaration.